Louis Vuitton Counterfeit Label Analysis [Lotus testing]
by: Ryan Fattini | SpotFakeHandbags.com | 6/15/12


Luxury_designer counterfeiting is a multi-billion dollar industry
[1], and the House of
Louis Vuitton is
perpetually in the cross-hairs
of the most well funded counterfeit operations[2][4]. Therefore counterfeit detection solutions
are imperative for consumer protection. When concerning Louis Vuitton, we argue that
the heat stamped Louis Vuittonlabel (or Louis Vuittonfont) should be considered ground zero for any rigorous
authentication. Our
Lotus,
application will test L.V. items (of unknown origin) for counterfeit signatures by
targeting specific heat stamp font deviations against an authentic
Louis Vuittonlabel template.
The Lotus argument is expressed by first considering L as the width (vector) of the L_font, and O as the width of the O_font (in Louis). Based on a small initial sample of authentic LV_font comparisons, it appears that many of the contemporary (21st) century O_fonts (in Louis) run roughly twice the distance of the previous L_font [3]. Further, the height of the contemporary L_font appears to come in around 2.2 x the width of the L_font such that if we will apply the value 2.2 to H it can be said that, H*L=Lheight, and further, that O=2L. Therefore by combining these arguments we can produce the expression, HL = Lheight = O H⁄2, which then becomes the root of the Lotus argument.
(i) However, due to the slight variance that exists within the Louis Vuittonfont templates - targets are not exact match, rather Lotus will target a range (Ω)[3].
Figure I: Louis Vuitton LO template (right) extracted from an authentic Louis Vuittonlogo (left).
 →
→
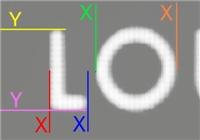
The table [A] below details nine label test runs through the Lotus application along with the extracted LOtemplate from [Figure I].
Note that the Accuracyrate is a threshold for authentic fonts, such that an Arate below 98 is considered a red flag. The Arate is determined when we consider the amount that the terminal point of 2L and HL either exceeds or falls short of the target zone. We will consider this value M (miss). Such that, AR = 100 - |ML|N + |MLheight|
(i)N=10
Table A: Lotus beta testing results.
Summary: The Lotus test filters out many counterfeit fonts, however, image distortion will play a significant role in the outcomes. The Lotus application is most accurate with 21st century heat stamps as Louis Vuittonvintage merchandise has a much higher degree of variance. Also, authentic fonts were identified that appear to deviate from the Lotus argument, and adjustments were made for merchandise with specific date-codes (SD). The majority of these deviations may map to the country of origin (and/or the model), in which case this information can be incorporated into the Lotus argument in order to execute a universal application concerning the contemporary LVfont.
Resources:
[1]: http://tv.ibtimes.com/luxury-brands-wage-war-against-the-multi-billion-dollar-counterfeit-industry/5838.html
[2]: http://www.komonews.com/news/local/Customs-officers-cracking-down-on-counterfeit-goods-143424926.html
[3]: http://spotfakehandbags.com/louis-vuitton-label-font-stamp-spot-fake.html
[4]: http://www.louisvuitton.com/front/#/eng_US/faq
Copyright © spotfakehandbags.com 2012-2013, All rights reserved. PRIVACY POLICY | Site Nav
The Lotus argument is expressed by first considering L as the width (vector) of the L_font, and O as the width of the O_font (in Louis). Based on a small initial sample of authentic LV_font comparisons, it appears that many of the contemporary (21st) century O_fonts (in Louis) run roughly twice the distance of the previous L_font [3]. Further, the height of the contemporary L_font appears to come in around 2.2 x the width of the L_font such that if we will apply the value 2.2 to H it can be said that, H*L=Lheight, and further, that O=2L. Therefore by combining these arguments we can produce the expression, HL = Lheight = O H⁄2, which then becomes the root of the Lotus argument.
(i) However, due to the slight variance that exists within the Louis Vuittonfont templates - targets are not exact match, rather Lotus will target a range (Ω)[3].
Figure I: Louis Vuitton LO template (right) extracted from an authentic Louis Vuittonlogo (left).
 →
→

The table [A] below details nine label test runs through the Lotus application along with the extracted LOtemplate from [Figure I].
Note that the Accuracyrate is a threshold for authentic fonts, such that an Arate below 98 is considered a red flag. The Arate is determined when we consider the amount that the terminal point of 2L and HL either exceeds or falls short of the target zone. We will consider this value M (miss). Such that, AR = 100 - |ML|N + |MLheight|
(i)N=10
Table A: Lotus beta testing results.
 |
X: 49 X: 87 X: 96 X: 177 Y: 110 Y: 29 X-axis: [75.735] 76[86.265] Y-axis: pass Accuracy rate: 99.99 |
Notes: Template image ZHiRes = .065 [O - (O*ZHiRes)] ≤ Target (Z)one ≤ [O + (O*ZHiRes)] |
 |
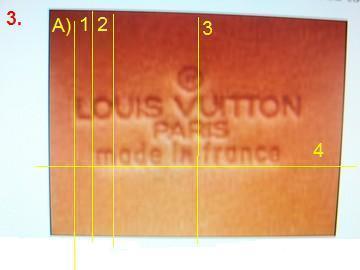
X: 15 X: 35 X: 30 X: 73 Y: 413 Y: 349 X-axis: [39.56] 40[46.44] Y-axis: +9 Accuracy rate: 91 |
Notes: Counterfeit test label Z = .08 [O - (O*Z)] ≤ Target (Z)one ≤ [O + (O*Z)] |
 |
X: 80 X: 86 X: 86 X: 93 Y: 379 Y: 369 X-axis: +4.44 Y-axis: -1.1 Accuracy rate: 55 |
Notes:
Counterfeit test label Z = .08 [O - (O*Z)] ≤ Target (Z)one ≤ [O + (O*Z)] |
 |
X: 42 X: 51 X: 51.3 X: 63 Y: 355 Y: 340 X-axis: +5.36 Y-axis: -1.65 Accuracy rate: 45 |
Notes: Counterfeit test label Z = .08 [O - (O*Z)] ≤ Target (Z)one ≤ [O + (O*Z)] |
 |
X: 60 X: 74 X: 76 X: 100 Y: 359 Y: 336 X-axis: +2.08 Y-axis: -2.9 Accuracy rate: 76 |
Notes: Counterfeit test label Z = .08 [O - (O*Z)] ≤ Target (Z)one ≤ [O + (O*Z)] |
 |
X: 38.3 X: 46 X: 46 X: 60 Y: 373 Y: 357 X-axis: +.28 Y-axis: pass Accuracy rate: 97.2 |
Notes: Counterfeit test label Z = .08 [O - (O*Z)] ≤ Target (Z)one ≤ [O + (O*Z)] Manual value input (.3) |
 |
X: 55 X: 60 X: 61 X: 70 Y: 388 Y: 397 X-axis: +.28 Y-axis: -.25 Accuracy rate: 97 |
Notes: Counterfeit test label Z = .08 [O - (O*Z)] ≤ Target (Z)one ≤ [O + (O*Z)] |
 |
X: 56 X: 60 X: 61 X: 69 Y: 358 Y: 338 X-axis: [7.36] 8 [8.64] Y-axis: +9 Accuracy rate: 91 |
Notes: Counterfeit test label Z = .08 [O - (O*Z)] ≤ Target (Z)one ≤ [O + (O*Z)] some image distortion issues, dist was corrected via resize |
 |
X: 54 X: 59 X: 57 X: 67 Y: 373 Y: 361 X-axis: [9.2] 10 [10.8] Y-axis: pass Accuracy rate: 99.9 |
Notes: Authentic test label Z = .08 [O - (O*Z)] ≤ Target (Z)one ≤ [O + (O*Z)] |
 |
X: 40 X: 47 X: 46 X: 60 Y: 372 Y: 361 X-axis: [12.88] 14 [15.12] Y-axis: -1.95 Accuracy rate: 98.05 |
Notes: Authentic test label Z = .08 [O - (O*Z)] ≤ Target (Z)one ≤ [O + (O*Z)] image corruption compressed L height, img was resized |
Summary: The Lotus test filters out many counterfeit fonts, however, image distortion will play a significant role in the outcomes. The Lotus application is most accurate with 21st century heat stamps as Louis Vuittonvintage merchandise has a much higher degree of variance. Also, authentic fonts were identified that appear to deviate from the Lotus argument, and adjustments were made for merchandise with specific date-codes (SD). The majority of these deviations may map to the country of origin (and/or the model), in which case this information can be incorporated into the Lotus argument in order to execute a universal application concerning the contemporary LVfont.
Resources:
[1]: http://tv.ibtimes.com/luxury-brands-wage-war-against-the-multi-billion-dollar-counterfeit-industry/5838.html
[2]: http://www.komonews.com/news/local/Customs-officers-cracking-down-on-counterfeit-goods-143424926.html
[3]: http://spotfakehandbags.com/louis-vuitton-label-font-stamp-spot-fake.html
[4]: http://www.louisvuitton.com/front/#/eng_US/faq
Copyright © spotfakehandbags.com 2012-2013, All rights reserved. PRIVACY POLICY | Site Nav